Physicochemical properties of enamel glazes
The physicochemical properties of enamel glaze are usually divided into the following categories:
I. Mechanical properties
Second, thermal properties
Three, optical properties
Four, chemical stability
Five, enamel other properties
Mechanical properties are subdivided into:
(A) tensile strength
(B) compressive strength
(C) flexural strength
(D) elasticity
(E) hardness
(F) density
(G) impact strength
(H) Adhesion strength
In the first two issues, we introduced the mechanical properties of tensile strength, compressive strength, flexural strength, elasticity, hardness and density, in this issue, we will introduce the impact strength and adhesion strength of enamel.
(E) Hardness

Hardness is the ability of the object to resist other objects carved or pressed into its surface. Hardness is expressed by: Mohs hardness (scratch method), micro hardness (indentation method), grinding hardness (abrasion method), etc. According to the different measurement methods used, the hardness value of enamel varies, and the hardness of enamel is generally measured by Mohs hardness.
The general enamel layer of Mohs hardness is 5 to 7 levels.
The hardness of the enamel has a great relationship with the composition of its formula, Na2O, K2O, PbO, etc. will make the hardness of the enamel lower; CaO, MgO, BaO, ZnO, Li2O, etc. can make the hardness of the enamel higher. In aluminosilicate system enamel, replacing SiO2 with Al2O3 can make the hardness increase. In boro-aluminate, when n(Na2O)/n(B2O3)>3, if Al2O3 replaces part of SiO2, the hardness increases; when n(Na2O)/n(B2O3)<1, if Al2O3 also replaces SiO2 the hardness will be reduced.
Grinding plus the introduction of quartz, clay, zirconia, sodium meta-antimonate, etc. will make the enamel hardness increase. Adding too much electrolyte, especially if it causes the enamel surface to boil, will make the hardness drop greatly.
In general, enamels with high hardness have better acid resistance than those with low hardness.
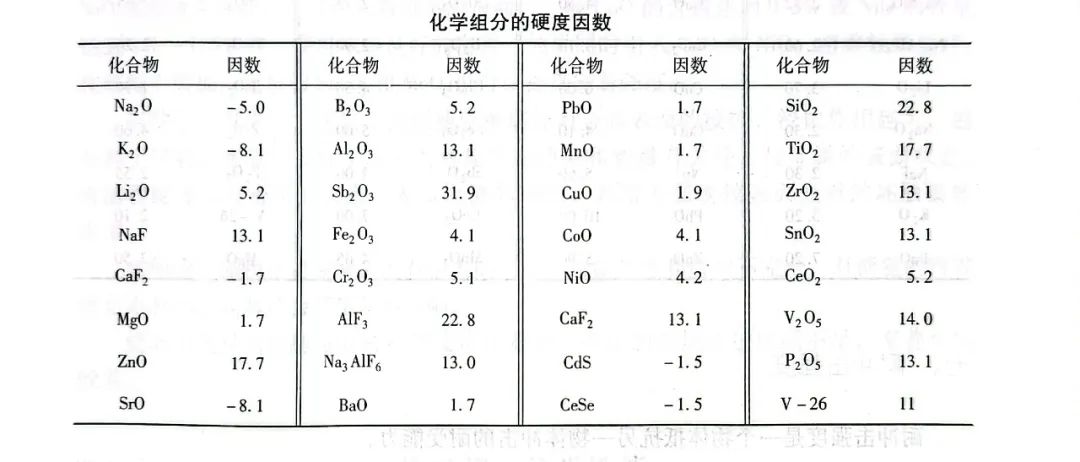
In a certain range, the hardness of porcelain enamel can be calculated according to the following formula:
Hm=(w1H1+W2H2+... +wnHn)/250
Where: Hm - porcelain enamel Mohs hardness;
wn - the mass fraction of each chemical component of the enamel;
Hn - the hardness factor of each chemical component of porcelain enamel (see the following table).
(D) density
General porcelain glaze density in 2.3 ~ 2.7g/cm3. special enamel, such as aluminum enamel and lead glaze density up to 3 ~ 5g/cm3. to disperse the gas phase for the emulsion of porcelain glaze density is less than 2.3g/cm3.
The density of porcelain enamel depends mainly on its chemical composition. Recipe in the density of the material, such as SiO2, B2O3, P2O5, BaO, PbO content increases, the density of porcelain enamel also becomes larger; density of small alkali metal oxides, or some alkaline earth metal oxides content increases, the density of porcelain enamel becomes smaller.
The density of porcelain enamel is related to the melting temperature and melting time. When the chemical composition is the same, the melting temperature is high or time is long (usually called melt over) of the enamel than the melting temperature is low or time is short (usually called melt incomplete) of the enamel density.
If a variety of grinding plus the same amount of grinding, density of porcelain glaze ground into a slurry, its stay performance than the density of small porcelain glaze glaze slurry to be poor.
The density of porcelain glaze, within a certain range, can be calculated by the following formula
ρ=m/V
Where: ρ - the density of porcelain glaze (g / cm3)
m - the mass of the molten block in the air;
V - the volume of the molten block.
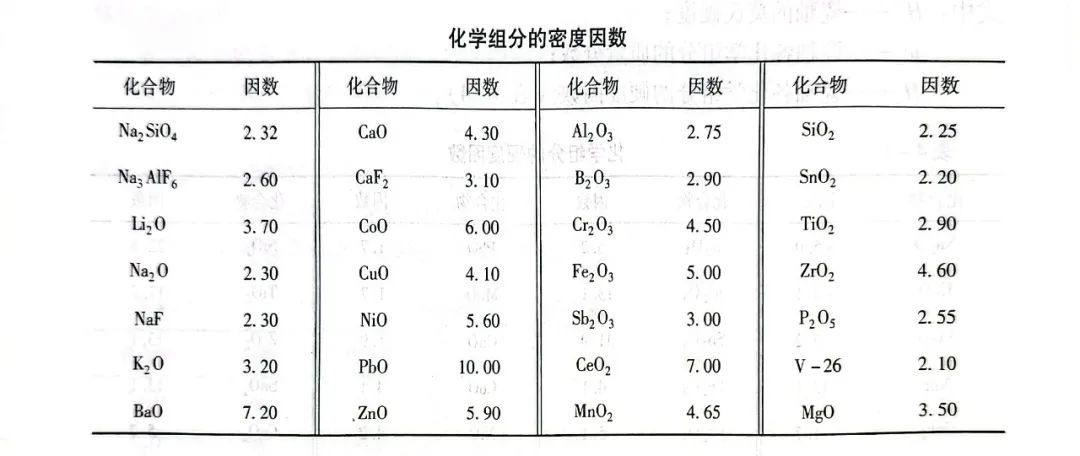
The density of porcelain enamel can also be approximated by the chemical composition, see Eq:
ρ = 100/(w1/ρ1 + w2/ρ2 + -... + wn/ρn)
where: wn - the mass fraction of each chemical component of porcelain enamel;
ρn - the density factor of each chemical component of the enamel.
Today's introduction ends here, we will continue to update the subsequent, welcome to follow us, bring you more knowledge of glass-lined glaze ~






